Convertion¶
This section shows the mapping between Fits and HDF5 formats, and following with the design of two H5Boss Formats,
- The Mapping Diagram helps to visualize the mapping between Fits and HDF5.
- The Mapping Table contains more detailed information of the relationship between the Boss-Fits structure and the Boss-HDF5 hierarchy.
- The Example Codes helps to understand ‘what is the difference in reading a’Flux’ dataset in the two formats’, etc.
Mapping Diagram¶
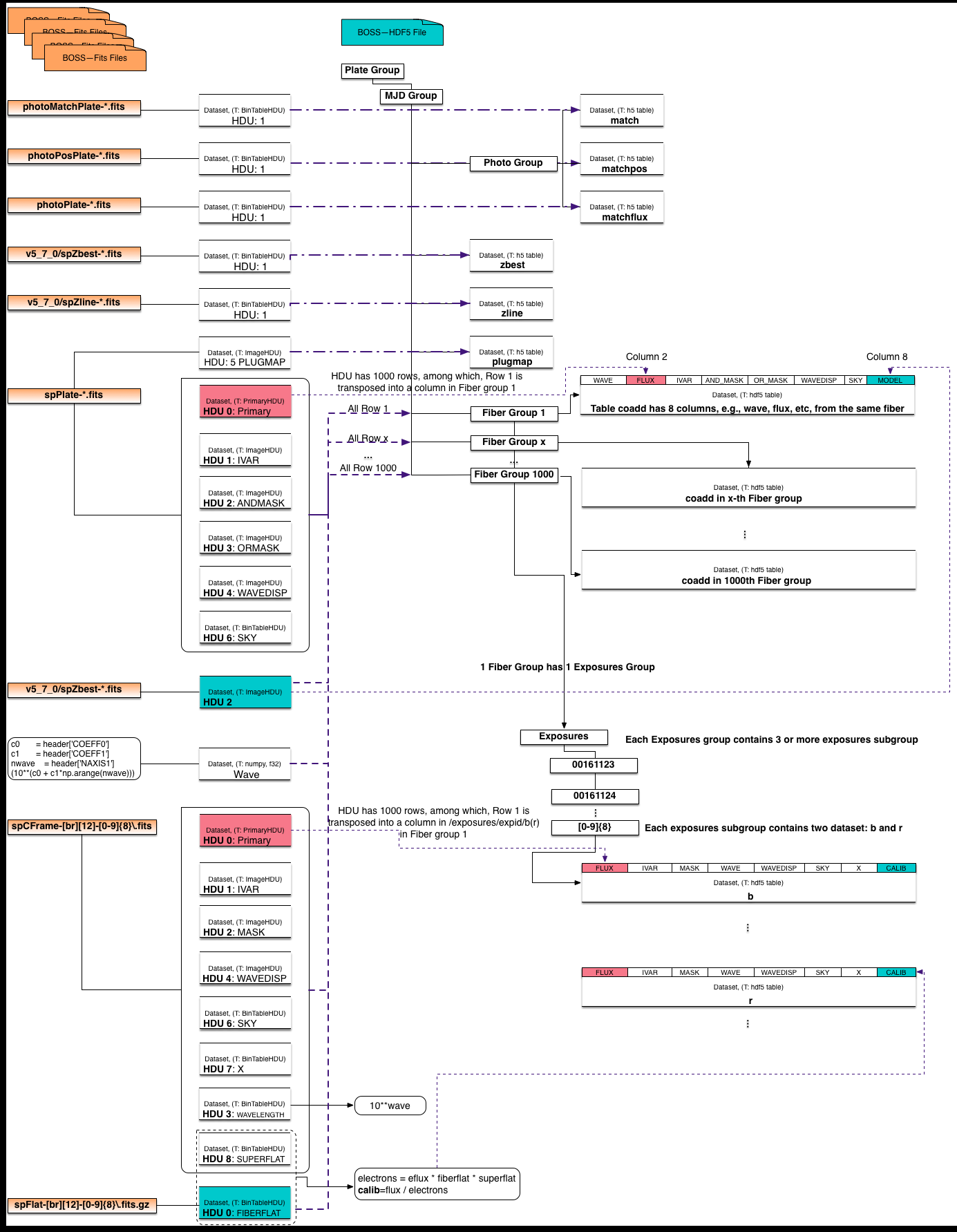
Mapping Table¶
The conversion code, took all files in a PLATE folder and convert into a single HDF5 file. Note that the BOSS data on NERSC project file system is organized as:
Fits Folder Top Level:
user@edison12: pwd
/global/projecta/projectdirs/sdss/data/sdss/dr12/boss/spectro/redux/v5_7_0
user@edison12: ls
3520 4032 4458 4848 5338 5897 6375 6758
3523 4033 4459 4849 5339 5898 6376 6759
3536 4034 4460 4850 5340 5899 6377 6760
3537 4035 4461 4851 5341 5900 6378 6780
3538 4036 4462 4852 5342 5901 6379 6781
3540 4037 4463 4853 5343 5902 6380 6782
3548 4038 4464 4854 5344 5903 6381 6783
...
...
Then inside one folder, which is named afte the PLATE number, e.g., plate 4857:
Fits Folder Second Level:
4857/
photoMatchPlate-4857-55711.fits spFluxcalib-r2-00131416.fits.gz
photoPlate-4857-55711.fits spFluxcalib-r2-00131417.fits.gz
photoPosPlate-4857-55711.fits spFluxcalib-r2-00131418.fits.gz
redux-4857-55711 spFluxcalib-r2-00131419.fits.gz
redux-4857-55711.o22925 spFluxcorr-b1-00131415.fits.gz
... ...
spCFrame-b1-00131415.fits spFluxcorr-b2-00131415.fits.gz
spCFrame-b1-00131416.fits spFluxcorr-b2-00131416.fits.gz
spCFrame-r2-00131415.fits spFluxdistort-4857-55711.fits
spCFrame-r2-00131416.fits spFluxdistort-4857-55711.ps
spCFrame-r2-00131417.fits spFrame-b1-00131415.fits.gz
spCFrame-r2-00131418.fits spFrame-b1-00131416.fits.gz
spFluxcalib-b2-00131417.fits.gz spFrame-r2-00131418.fits.gz
spFluxcalib-b2-00131418.fits.gz spFrame-r2-00131419.fits.gz
spFluxcalib-r1-00131416.fits.gz spPlate-4857-55711.fits
spFluxcalib-r1-00131417.fits.gz spSN2d-4857-55711.ps
spFluxcalib-r1-00131418.fits.gz spSN2d-4857-55711.ps.orig
spFluxcalib-r1-00131419.fits.gz spectro_redux_v5_7_0_4857.sha1sum
spFluxcalib-r2-00131415.fits.gz v5_7_0
After the conversion, the whole folder 4857 becomes a single HDF5 file, in which, there are 1000 fiber groups and a few catalog datasets.
HDF5 Folder Top Level:
user@edison12: pwd
$SCRATCH/h5boss/v5_7_0
user@edison12: ls
3520.h5 4032.h5 4458.h5 4848.h5 5338.h5 5897.h5 6375.h5 6758.h5
3523.h5 4033.h5 4459.h5 4849.h5 5339.h5 5898.h5 6376.h5 6759.h5
3536.h5 4034.h5 4460.h5 4850.h5 5340.h5 5899.h5 6377.h5 6760.h5
3537.h5 4035.h5 4461.h5 4851.h5 5341.h5 5900.h5 6378.h5 6780.h5
3538.h5 4036.h5 4462.h5 4852.h5 5342.h5 5901.h5 6379.h5 6781.h5
3540.h5 4037.h5 4463.h5 4853.h5 5343.h5 5902.h5 6380.h5 6782.h5
3548.h5 4038.h5 4464.h5 4854.h5 5344.h5 5903.h5 6381.h5 6783.h5
...
...
For the catalog, the conversion simply reads one HDU in a fits file and writes into a table dataset in HDF5. For example, as shown in the following catalog mapping table, the HDU1 in ‘photoMatchPlate-pppp-mmmmm.fits’ becomes a HDF5 dataset within the ‘photo’ group, where the higher level groups are ‘plate’ and ‘mjd’.
Catalog:
| Fits File | Fits HDU | HDF5 Group | HDF5 Dataset |
|---|---|---|---|
| photoMatchPlate-pppp-mmmmm.fits | HDU 1 | plate/mjd/photo | match |
| photoPosPlate-pppp-mmmmm.fits | HDU 1 | plate/mjd/photo | matchpos |
| photoPlate-pppp-mmmmm.fits | HDU 1 | plate/mjd/photo | matchflux |
| v5_7_0/spZbest-pppp-mmmmm.fits | HDU 1 | plate/mjd | zbest |
| v5_7_0/spZline-pppp-mmmmm.fits | HDU 1 | plate/mjd | zline |
| spPlate-pppp-mmmmm.fits | HDU 5 | plate/mjd | plugmap |
In each of the 1000 fiber groups, the fiber number is used as the group name in HDF5, e.g., 1, which is under ‘plate/mjd’. In a fiber group, there is a ‘coadd’ dataset, which is a 4000*8 2D array,(the number 4000 varies in different plates). The number 8 refers to the total number of wavelengths that’re converted, i.e., Flux, Ivar, and_mask, or_mask, wavedisp, wave, sky and model. These wavelengths are from different HDUs of the ‘spPlate-pppp-mmmmm.fits’ file. For example, the ‘Flux’ is from the Primary HDU. In fits, this primary HDU is a 1000 by 4000 2D table, in HDF5 file, this 2D table is split into 1000 fiber groups, where each fiber group only has the wavelength of one fiber. Similar convertion was conducted on the ‘Exposures’, which is from ‘spCFrame-[br][12]-[0-9]{8}.fits’ file. Special attention needs to be paid on the column ‘wave’ in coadd, and columns ‘wave’ and ‘clib’ in the b/r dataset, as noted below the table.
Spectra:
| Id | Fits File | Fits HDU | HDF5 Group | HDF5 Dataset(ColumnID) ColumnName |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | spPlate-pppp-mmmmm.fits | HDU 0 | plate/mjd/[1-1000] | coadd(col2) FLUX |
| 2 | spPlate-pppp-mmmmm.fits | HDU 1 IVAR | plate/mjd/[1-1000] | coadd(col3) IVAR |
| 3 | spPlate-pppp-mmmmm.fits | HDU 2 ANDMASK | plate/mjd/[1-1000] | coadd(col4) AND_MASK |
| 4 | spPlate-pppp-mmmmm.fits | HDU 3 ORMASK | plate/mjd/[1-1000] | coadd(col5) OR_MASK |
| 5 | spPlate-pppp-mmmmm.fits | HDU 4 WAVEDISP | plate/mjd/[1-1000] | coadd(col6) WAVEDISP |
| 6 | spPlate-pppp-mmmmm.fits | HDU 5 PLUGMAP | plate/mjd/[1-1000] | coadd(col1)* WAVE |
| 7 | spPlate-pppp-mmmmm.fits | HDU 6 SKY | plate/mjd/[1-1000] | coadd(col7) SKY |
| 8 | plate/mjd/[1-1000] | coadd(col8) MODEL | ||
| 9 | spCFrame-[br][12]-[0-9]{8}.fits | HDU 0 | plate/mjd/[1-1000]/exposures/[0-9]{8} | b/r(col1) FLUX |
| 10 | spCFrame-[br][12]-[0-9]{8}.fits | HDU 1 IVAR | plate/mjd/[1-1000]/exposures/[0-9]{8} | b/r(col2) IVAR |
| 11 | spCFrame-[br][12]-[0-9]{8}.fits | HDU 2 MASK | plate/mjd/[1-1000]/exposures/[0-9]{8} | b/r(col3) MASK |
| 12 | spCFrame-[br][12]-[0-9]{8}.fits | HDU 3 WAVELENGTH | plate/mjd/[1-1000]/exposures/[0-9]{8} | b/r(col4)* WAVE |
| 13 | spCFrame-[br][12]-[0-9]{8}.fits | HDU 4 WAVEDISP | plate/mjd/[1-1000]/exposures/[0-9]{8} | b/r(col5) WAVEDISP |
| 14 | spCFrame-[br][12]-[0-9]{8}.fits | HDU 6 SKY | plate/mjd/[1-1000]/exposures/[0-9]{8} | b/r(col6) SKY |
| 15 | spCFrame-[br][12]-[0-9]{8}.fits | HDU 7 X | plate/mjd/[1-1000]/exposures/[0-9]{8} | b/r(col7) X |
| 16 | spCFrame-[br][12]-[0-9]{8}.fits | HDU 8 SUPERFLAT | plate/mjd/[1-1000]/exposures/[0-9]{8} | b/r(col8)* CLIB |
| 17 | spFlat-[br][12]-[0-9]{8}.fits.gz | HDU 0 FIBERFLAT | plate/mjd/[1-1000]/exposures/[0-9]{8} | b/r(col8)* CLIB |
Notes: The convertion simply copy the data in fits file and reorginze in HDF5 file, a few exceptions where the data need additional calculation can be better understood by reading the code. Here are just brief descriptions:
line 8, This wave column is obtained with the following python code:
header = fits.open(platefile)[0].header
c0 = header['COEFF0']
c1 = header['COEFF1']
nwave = header['NAXIS1']
wave = (10**(c0 + c1*np.arange(nwave)))
line 12, wavelength is log based, so the conversion code calculates the reverse, i.e., ‘WAVE’=10^wavelength
line 16 and 17, the ‘CLIB’ is calculated with the following python code:
electrons = eflux * fiberflat * superflat
calib = flux / electrons
Example Codes¶
The sample codes for reading same data from Fits versus from the converted HDF5 file:
Read plate: 4857, mjd: 55711, fiber: 4, FLUX
Read Flux from Fits:
dfits = fitsio.FITS('spPlate-4857-55711.fits')
dflux = dfits[0][3:4,:]
Read Flux from HDF5:
dh5 = h5py.File('4857-55711.h5')
dflux = dh5['4857/55711/4/coadd']['FLUX']
Read Multiple HDUs from Fits:
dfits = fitsio.FITS('spPlate-4857-55711.fits')
dflux = dfits[0][3:4,:]
dwave = dfits[1][3:4,:]
Read Multiple HDUs from HDF5:
dh5 = h5py.File('4857-55711.h5')
dflux_wave = dh5['4857/55711/4/coadd'][('FLUX','IVAR')]
Read All HDUs from Fits:
for i in range(0,6):
dall[i] = dfits[i][3:4,:]
Read All HDUs from HDF5:
dall = dh5['4857/55711/4/coadd'][()]